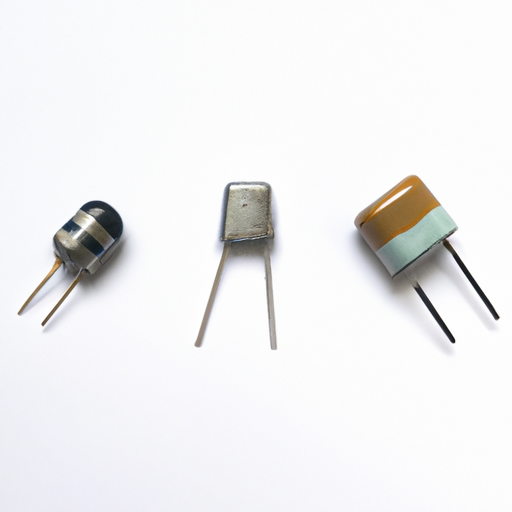
Popular Models of Common Fuse Resistors
I. Introduction
In the world of electronics, the components we choose can significantly impact the performance and safety of our devices. One such component that plays a crucial role in protecting circuits from overcurrent conditions is the fuse resistor. This article will delve into the definition, functionality, and various types of fuse resistors, as well as highlight popular models from leading manufacturers. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of fuse resistors and their applications in modern electronics.
II. Understanding Fuse Resistors
A. What is a Fuse Resistor?
A fuse resistor is a specialized component that combines the functions of a resistor and a fuse. Its primary purpose is to limit current flow while also providing overcurrent protection. When the current exceeds a predetermined threshold, the fuse resistor will "blow," effectively interrupting the circuit and preventing damage to other components.
1. Functionality and Purpose
The main functionality of a fuse resistor is to protect sensitive electronic components from excessive current. Unlike standard resistors, which are designed to dissipate energy as heat, fuse resistors are engineered to fail safely when subjected to overcurrent conditions. This unique characteristic makes them invaluable in various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery.
2. Differences Between Fuse Resistors and Standard Resistors
While both fuse resistors and standard resistors are used to control current flow, their operational principles differ significantly. Standard resistors are designed to maintain a constant resistance value under normal operating conditions, while fuse resistors are designed to change state (from conductive to non-conductive) when a specific current threshold is exceeded. This ability to "blow" makes fuse resistors a critical safety feature in many electronic designs.
B. How Fuse Resistors Work
1. Mechanism of Operation
The operation of a fuse resistor is based on its thermal and electrical characteristics. When current flows through the fuse resistor, it generates heat due to its resistance. If the current exceeds the rated limit, the heat generated will cause the resistor to reach a critical temperature, leading to its failure. This failure interrupts the circuit, protecting downstream components from damage.
2. Thermal and Electrical Characteristics
Fuse resistors are designed with specific thermal and electrical characteristics that dictate their performance. These include power ratings, resistance values, and temperature coefficients. Understanding these characteristics is essential for selecting the right fuse resistor for a given application.
III. Types of Fuse Resistors
A. Wirewound Fuse Resistors
1. Construction and Materials
Wirewound fuse resistors are constructed using a wire wound around a ceramic or insulating core. This design allows for high power ratings and excellent thermal stability. The wire is typically made from materials like nickel-chromium or copper-nickel alloys.
2. Advantages and Disadvantages
The primary advantage of wirewound fuse resistors is their ability to handle high power levels and provide precise resistance values. However, they can be bulkier than other types and may have slower response times.
B. Thick Film Fuse Resistors
1. Manufacturing Process
Thick film fuse resistors are made by applying a thick layer of resistive material onto a substrate, typically ceramic. This process allows for mass production and cost-effectiveness.
2. Applications and Performance
Thick film fuse resistors are commonly used in applications where space is limited, such as in surface-mounted devices (SMDs). They offer good performance in terms of stability and reliability.
C. Thin Film Fuse Resistors
1. Characteristics and Benefits
Thin film fuse resistors are made by depositing a thin layer of resistive material onto a substrate. They offer high precision and low temperature coefficients, making them ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances.
2. Use Cases in Modern Electronics
Thin film fuse resistors are often used in high-frequency applications, precision measurement devices, and advanced electronic circuits where performance is critical.
IV. Popular Models of Fuse Resistors
A. Overview of Leading Manufacturers
Several manufacturers are known for producing high-quality fuse resistors. Among them, Vishay, Bourns, and Ohmite stand out for their innovative designs and reliable products.
B. Detailed Examination of Popular Models
1. Vishay's FUS Series
Specifications: The FUS series from Vishay offers a range of power ratings from 0.5W to 5W, with resistance values from 1Ω to 1MΩ. They feature a tolerance of ±5% and a temperature coefficient of ±100 ppm/°C.
Applications: These fuse resistors are widely used in consumer electronics, automotive applications, and industrial equipment.
2. Bourns' 0.5W Series
Specifications: Bourns' 0.5W series provides a compact design with resistance values ranging from 1Ω to 100kΩ. They have a tolerance of ±5% and are designed for surface mount applications.
Applications: This series is ideal for use in telecommunications and portable devices where space is a premium.
3. Ohmite's 1W Series
Specifications: Ohmite's 1W series features a power rating of 1W, with resistance values from 0.1Ω to 1MΩ. They offer a tolerance of ±1% and are designed for high-performance applications.
Applications: These fuse resistors are commonly used in industrial equipment and medical devices, where reliability is paramount.
C. Comparison of Features and Performance
When comparing fuse resistors, several factors come into play:
1. Power Ratings
Power ratings determine how much power a fuse resistor can handle before it fails. Higher power ratings are essential for applications with significant current flow.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels indicate the precision of the resistance value. Lower tolerance levels are preferred in applications requiring high accuracy.
3. Temperature Coefficients
Temperature coefficients measure how much the resistance value changes with temperature. A lower temperature coefficient is desirable for stable performance across varying environmental conditions.
V. Applications of Fuse Resistors
Fuse resistors find applications across various industries, including:
A. Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, fuse resistors protect sensitive components from overcurrent conditions, ensuring device longevity and reliability.
B. Automotive Applications
In automotive systems, fuse resistors are used to safeguard electronic control units (ECUs) and other critical components from electrical faults.
C. Industrial Equipment
Industrial machinery often employs fuse resistors to prevent damage from surges and overloads, enhancing operational safety.
D. Telecommunications
In telecommunications, fuse resistors protect communication devices from electrical disturbances, ensuring uninterrupted service.
E. Medical Devices
In medical devices, reliability is crucial. Fuse resistors help protect sensitive electronic components, ensuring patient safety and device functionality.
VI. Selecting the Right Fuse Resistor
A. Factors to Consider
When selecting a fuse resistor, consider the following factors:
1. Power Rating
Ensure the power rating meets or exceeds the expected current flow in your application.
2. Resistance Value
Choose a resistance value that aligns with your circuit requirements.
3. Environmental Conditions
Consider the operating environment, including temperature and humidity, to select a fuse resistor with appropriate thermal characteristics.
B. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid selecting a fuse resistor with insufficient power ratings or incorrect resistance values, as this can lead to circuit failure.
C. Tips for Proper Installation and Use
Ensure proper installation by following manufacturer guidelines and using appropriate soldering techniques to avoid damaging the component.
VII. Future Trends in Fuse Resistor Technology
A. Innovations in Materials and Design
The future of fuse resistors lies in advancements in materials and design, leading to more compact and efficient components.
B. Increasing Demand in Emerging Technologies
As technology evolves, the demand for fuse resistors in emerging fields such as renewable energy and electric vehicles is expected to grow.
C. Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices, developing eco-friendly materials and production methods for fuse resistors.
VIII. Conclusion
In summary, fuse resistors are essential components in modern electronics, providing both current limiting and overcurrent protection. Understanding the various types, popular models, and their applications can help you make informed decisions when selecting fuse resistors for your projects. As technology continues to advance, staying informed about the latest trends and innovations in fuse resistor technology will be crucial for engineers and designers alike.
IX. References
- Manufacturer websites and technical datasheets
- Industry publications and research articles on fuse resistors
- Online electronics forums and communities for practical insights and experiences
By exploring the world of fuse resistors, you can enhance your understanding of this critical component and its role in ensuring the safety and reliability of electronic devices.